
Actuarial science and claims experience allow these insurance companies to price their policies so insurance purchasers will live long enough on average to allow the insurer to earn a profit. Individuals might buy an annuity without clearly understanding how they work or the costs involved. It’s important to do your research to ensure that you understand all fees, charges, expenses, and potential penalties.
Table of Contents
- The contracts are not registered under the Securities Act of 1933 and are offered and sold in reliance on an exemption therein.
- Annuities deal with longevity risk or the risk of outliving one’s assets.
- With ordinary annuities, payments are made at the end of a specific period.
- Again, the amount you receive can depend on several factors, such as your age, gender, whether it’s a single or joint policy and more.
- Because annuity rates are constant, you can quickly arrive at these values by using annuity tables.
The product is appropriate provided that the purchaser understands that they’re trading a liquid lump sum for a guaranteed series of cash flows. Annuity factors primarily calculate the present value of future annuity payments, helping determine whether a lump-sum payment or a series of future payments is more beneficial. This calculation sums future payments discounted by the appropriate interest rate. Most buyers of annuities aim to create a steady stream of income as retirement income.
How to Calculate the Future Value of an Annuity
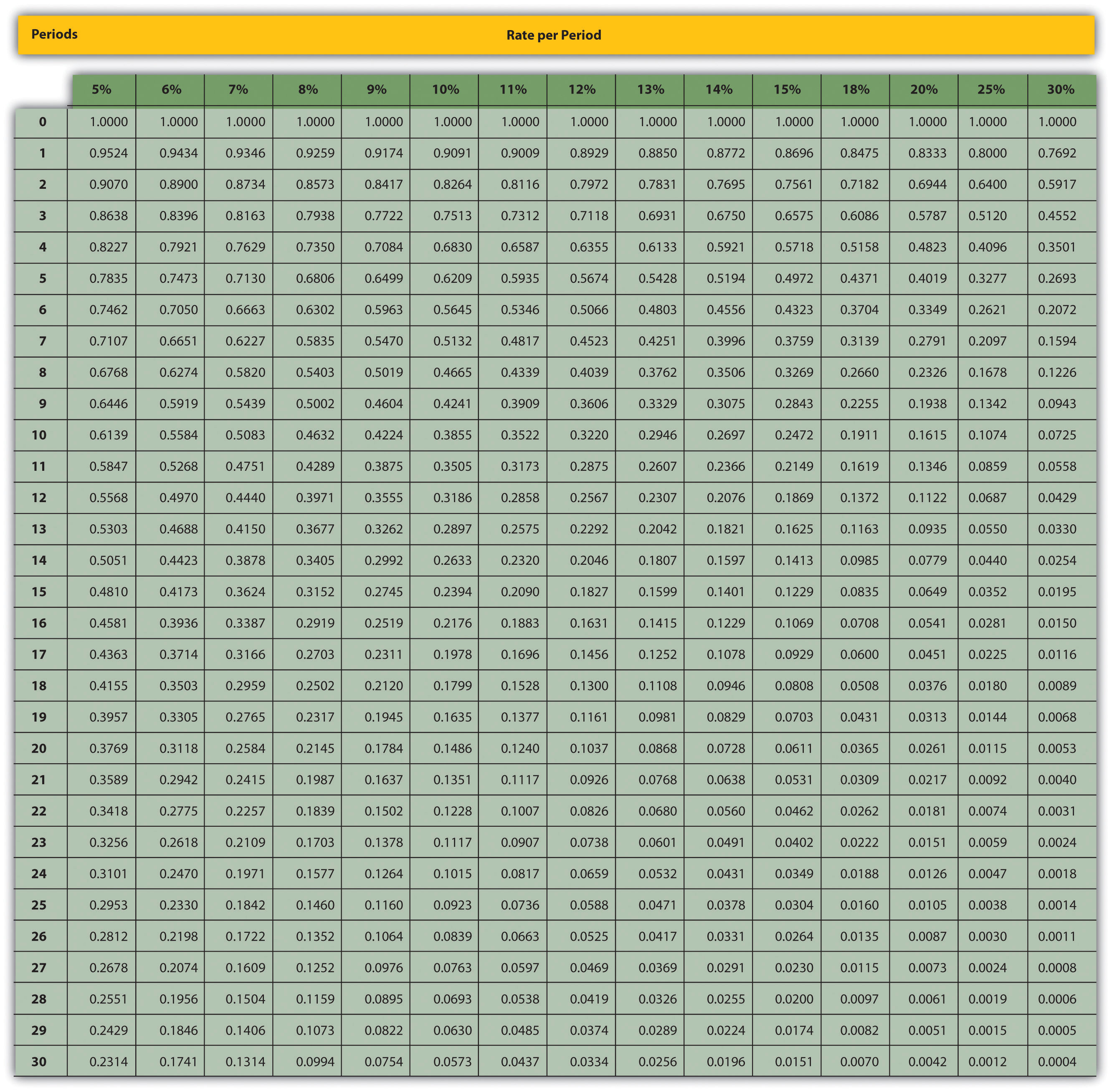
Suppose you want to determine the value today of receiving $1.00 at the end of each of the next 4 years. To solve this, we can construct a table that determines the present values of each of the receipts. By working with a trusted advisor, you can ensure that your retirement plan is tailored to your needs, maximizing your income and providing the financial security you deserve. Individual retirement accounts (IRAs) help people make early savings for post-retirement. Since it is primarily meant for savings, making withdrawals from the account might not be a great idea.
Using the Discount Rate for the Present Value Interest Factor
The present value interest factor may only be calculated if the annuity payments are for a predetermined amount spanning a predetermined range of time. Despite their potential for greater earnings, variable and indexed annuities are often criticized for their relative complexity and the fees that are charged for them. For example, there can be steep surrender charges if the buyer chooses to withdraw their money within the first few years of the contract.
These annuities also offer flexibility in choosing the desired annual income, making them a versatile option for retirement planning. Understanding the benefits of fixed index annuities with income riders helps in making more informed retirement strategy decisions. Fixed index annuities provide monthly income and offer a unique combination what is an annuity factor of benefits, providing a steady income stream throughout retirement. Annuity factors are invaluable for determining withdrawal amounts from retirement accounts without penalties, ensuring you don’t outlive your savings. The calculation also considers interest rates and the number of years, aiding in more effective withdrawal planning.
Say you own a fixed annuity that pays a set amount of $10,000 every year. The terms of your contract state that you will hold the annuity for seven years at a guaranteed effective interest rate of 3.25%. You’ve owned the annuity for five years and now have two annual payments left. The table simplifies this calculation by telling you the present value interest factor, accounting for how your interest rate compounds your initial payment over a number of payment periods. Grasping the present value annuity factor reveals the annuity’s monetary value if fully funded today, aiding in financial planning and understanding the maximum monthly payment possible with available funds. Having $10,000 today is better than being given $1,000 per year for the next 10 years because the sum could be invested and earn interest over that decade.
Such calculations and their results can add confidence to your financial planning and investment decision-making. The present value of an annuity refers to how much money would be needed today to fund a series of future annuity payments. Or, put another way, it’s the sum that must be invested now to guarantee a desired payment in the future. In contrast to the FV calculation, PV calculation tells you how much money would be required now to produce a series of payments in the future, again assuming a set interest rate. In addition, you have access to your account value should your circumstances change (surrender charges may apply and the guaranteed income amount will be reduced).
The more you deposit, typically, the larger your monthly payments will be. Only 36% of Americans saving for retirement expect to have enough to be financially secure when they retire, according to an AARP survey from January 2024. The biggest risk with most retirement planning is outliving your savings. An ordinary annuity is a series of recurring payments that are made at the end of a period, such as payments for quarterly stock dividends. An annuity due, by contrast, is a series of recurring payments that are made at the beginning of a period.
